Private Equity's Evolving Role in Energy Financing
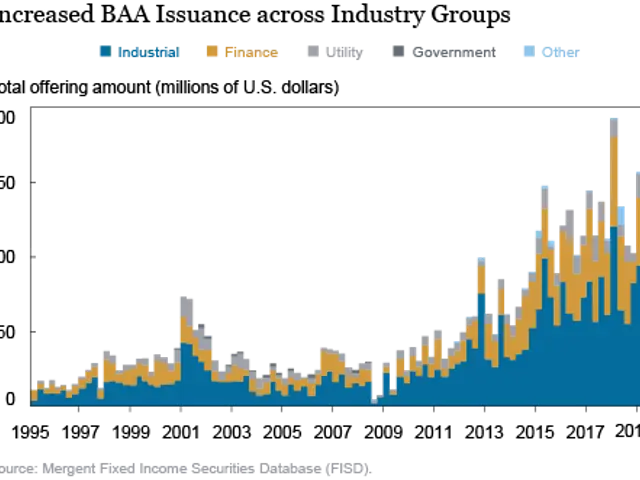
Private equity's role in energy financing has evolved significantly in recent years. While they've traditionally invested in fossil fuels, a shift towards renewable energy is evident, with $14.6 billion invested in 2023 alone. However, concerns persist about their involvement in fossil fuel financing, which may increase stranded asset risk.
Major global private equity firms have been acquiring large amounts of oil and gas assets from public markets since 2021, distancing themselves from public companies with carbon intensity reduction commitments. Despite the lack of specific firm names and acquisition data for this exact time frame, the trend is clear. This shift is partly driven by listed firms selling emission-intensive assets under pressure from shareholders to reduce their carbon footprint.
Private equity's involvement in renewable energy is growing, with a significant $14.6 billion invested in 2023. This increased activity in both fossil fuel and renewable energy financing makes private equity an increasingly relevant player in net zero capital allocations.
The flow of emission-intensive assets into private markets, facilitated by private equity, raises concerns about stranded assets due to the lack of viable exit strategies. As private equity continues to play a significant role in energy financing, both in fossil fuels and renewable energy, its impact on the transition to a low-carbon economy will be crucial to monitor.